Your cart is empty
Understanding OSR Instructions in PLC: A Comprehensive Guide

OSR (One Shot Rise) instructions are essential components in Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) that allow for the detection of a rising edge in an input signal. This instruction is crucial for capturing transient events, enabling the PLC to respond only once to a specific input condition. Understanding how OSR instructions function is vital for anyone involved in industrial automation, as they play a significant role in ensuring accurate and efficient control processes.
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) serve as the backbone of industrial automation, providing robust solutions for controlling machinery and processes across various sectors. Their primary role is to automate tasks that would otherwise require manual intervention, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and safety in operations. PLCs are designed to handle multiple inputs and outputs, processing data in real-time to execute commands based on programmed logic.
One of the key advantages of PLCs is their flexibility. They can be programmed to perform a wide range of functions, from simple tasks like turning on a motor to complex sequences involving multiple operations and feedback systems. This adaptability allows industries to tailor automation solutions to specific needs, leading to optimized workflows and increased productivity.
PLCs also contribute significantly to reducing downtime. In an industrial setting, even minor delays can lead to substantial financial losses. By automating processes and enabling real-time monitoring and control, PLCs help identify and address issues promptly, minimizing disruptions. Additionally, their ability to integrate with other automation technologies, such as Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs) and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems, further enhances their effectiveness in managing industrial operations.
Furthermore, PLCs are designed for rugged environments, capable of withstanding harsh conditions such as extreme temperatures, vibrations, and electromagnetic interference. This durability ensures that they can operate reliably even in demanding industrial settings, making them an indispensable tool in sectors like manufacturing, oil and gas, water treatment, and more.
In summary, PLCs play a crucial role in industrial automation by providing flexible, reliable, and efficient control solutions. Their ability to automate complex processes, minimize downtime, and withstand challenging conditions makes them essential for modern industrial operations.
How OSR Instruction Works in PLC Programming
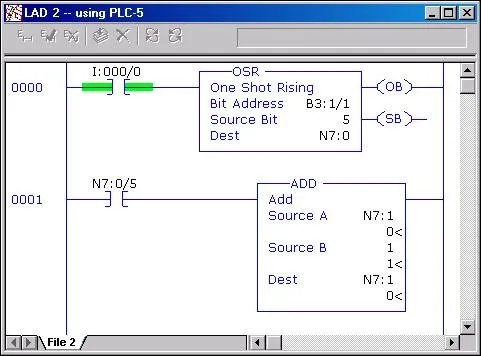
The One-Shot Rising (OSR) instruction is a crucial element in PLC programming that allows you to capture a single transition of an input signal. Essentially, it transforms a continuous signal into a fleeting one, triggering an output action just once for every rising edge of the input. This can be especially useful in scenarios where you only want an action to occur once, despite the ongoing input condition.
Here’s a breakdown of how the OSR instruction functions:
- Input Condition: The OSR instruction monitors a specific input for a rising edge. This means it looks for a transition from a low state (0) to a high state (1).
- Single Trigger: Upon detecting a rising edge, the OSR instruction sets its output to true (or high) for that single scan cycle.
- Reset State: After the scan cycle, the output returns to false (or low), regardless of the input state. This ensures that any subsequent high states on the input will not trigger the output again until the next rising edge.
To implement OSR effectively, it’s essential to consider the timing and frequency of the input signal. If the input signal fluctuates rapidly, the OSR instruction will still only activate once for each rising edge, making it a reliable tool for avoiding repetitive actions.
Examples of OSR Instruction in Real-World Applications

Using the OSR instruction in real-world applications can enhance automation efficiency in various industries. Here are some practical examples:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Conveyor Systems | In a conveyor system, OSR can be used to start a motor only when a product is detected on the sensor. This prevents multiple starts if the product remains on the sensor. |
| Batch Processing | In batch processing plants, OSR can trigger the addition of ingredients once when a batch starts, avoiding over-addition from continuous signals. |
| Safety Systems | OSR can be employed in safety systems to ensure alarms or safety mechanisms only activate once during an emergency event, preventing confusion from sustained input signals. |
| Data Logging | When collecting data from sensors, OSR ensures that data is recorded only once per event, providing accurate logs without duplicates. |
In summary, the OSR instruction is a powerful tool in PLC programming that allows for precise control and efficient automation. By understanding its functionality and real-world applications, you can leverage this instruction to improve your automation processes significantly.
Common Mistakes When Using OSR in PLCs
Using One-Shot Rising (OSR) instructions in PLCs can greatly enhance your control processes, but it’s easy to trip up and make mistakes. Here are some common pitfalls to avoid:
- Neglecting Debounce Logic: Many users forget to incorporate debounce logic when dealing with mechanical switches. This can lead to multiple triggers of the OSR instruction, causing erratic behavior.
- Improper Placement of OSR: Placing the OSR instruction in the wrong part of your logic can result in missed triggers or unintended activations. Always ensure it’s positioned correctly within the scan cycle.
- Assuming OSR Will Fix All Timing Issues: While OSR can help with timing, it won’t solve every synchronization issue. Relying solely on this instruction can lead to incomplete or faulty control strategies.
- Failing to Reset OSR: Forgetting to reset the OSR instruction after it has been triggered can lead to continuous activation, which can disrupt your process.
- Overlooking Documentation and Labeling: Not properly documenting your OSR usage can make troubleshooting difficult. Always label your OSR instructions clearly for easy reference.
Best Practices for Implementing OSR Instructions
To make the most of OSR instructions in your PLC programming, consider these best practices:
- Use Debounce Logic: Always incorporate debounce logic for inputs that can have noise or bouncing, such as mechanical switches. This ensures a clean, single trigger.
- Plan Your Logic Flow: Before implementing OSR, outline your control logic. Knowing where and how the OSR fits in will improve your program’s reliability.
- Regularly Test Your Code: Test your logic regularly in a controlled environment to ensure the OSR functions as intended under various conditions.
- Document Your Work: Clearly document where and why you are using OSR instructions in your program. This can be invaluable for future maintenance or troubleshooting.
- Limit OSR Usage: Use OSR instructions judiciously. Overusing them can complicate your logic and make it hard to read and maintain.
Understanding OSR Instructions in PLC: A Comprehensive Guide
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are crucial in automating industrial processes, and understanding their instructions is essential for effective programming. One such instruction is the One-Shot Rising (OSR) instruction, which plays a vital role in event-driven applications.
The OSR instruction is designed to detect a rising edge on its input. This means it will produce a true output (or a “1”) only once when the input transitions from false (0) to true (1). After triggering, the OSR resets itself on the next scan unless the input remains true, making it invaluable for capturing transient events.
Key characteristics of OSR instructions include:
- Edge Detection: OSR captures the moment an input switches from low to high.
- Single Trigger: It activates only once per rising edge, preventing multiple triggers during a sustained high state.
- Reset Mechanism: The instruction resets automatically under certain conditions, which can be defined by the programmer.
To implement OSR instructions effectively, consider the following:
| Consideration | Description |
|---|---|
| Input Conditions | Identify the specific conditions that will trigger the OSR instruction. |
| Timing | Ensure the timing of the input signal aligns with the OSR usage to prevent missed triggers. |
| Program Structure | Integrate OSR instructions within the program’s logic to maintain clarity and efficiency. |
In summary, mastering OSR instructions is essential for efficient PLC programming. By understanding their functionality and implementing them correctly, programmers can enhance the responsiveness and reliability of their control systems.